1. PRODUCT CERTIFICATION AND PRODUCT CHANGES
Products (aircraft, engines, propellers), as well as parts installed in them, require certification in accordance with applicable regulations.
The scope of certification is determined by the category of the aircraft.
After the certification, a Design approval (Type certificate, Supplemental type certificate and other minor and major changes or repairs) is issued by the competent authority (in the EU, this is EASA) or by Design Organisations accordingly their privileges.The certification of parts and equipment is part of the product certification and is part of the Type certificate or changes to Type certificate for the entire product. Equipment certified according to CS-ETSO and EASA Part 21, Subpart O is an exception.To achieve a product certification or to change a product certification, certain organizational requirements according to EASA Part 21 must be achieved.
Depending on the product categories, certifications can be achieved if the following organizational requirements (applications/organizational forms) are demonstrated:
- Demonstration of capabilities via certification program (21.A.14(c));
- Demonstration of capability via agreement to use alternative procedures (ADOA acc. to (21.A.14(b)));
- Demonstrate capabilities via design organization approval (DOA per (21.A.14(a))).
1.1. REQUIREMENTS AS BASIS OF CERTIFICATION OR CHANGE OF CERTIFICATION DEPENDING ON PRODUCT CATEGORY
- Certification specification (CS)
- Environmental protection specification
- Operational suitability data (OSD)
- Special conditions* (SC)
- Specific customer requirements
- Specific Operational requirements
- Industry standards
- Etc.
*Specified by EASA
1.2. VERIFICATION OF REQUIREMENT`S IMPLEMENTATION IN THE DESIGN OF A PRODUCT OR A MODIFICATION OF A PRODUCT OR A MODIFICATION OF PRODUCT
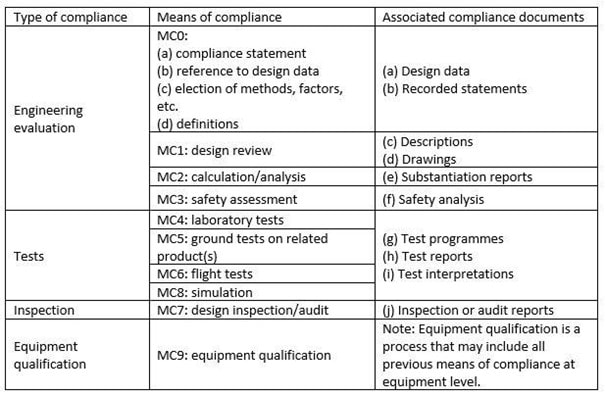
- Verification is planned and performed following to the established Means of Compliance (MoC) considering EASA LOI (Level of Involvement).
- Depending on product categories (e.g. complex or non-complex) or change (minor, major, major – significant) as well as design criticality quality and its novelty, safety analyses and assessments can be performed.
- Verification is based on design qualification through inspections and tests
MoC Categorization should be i.a.w. Appendix A to AMC 21.A.15 (b).
Exemplary representation of a certification process (rough) considering requirements from EASA Part 21, Subpart J (Design Management System) and ARP 4754 “Guidelines for development of civil Aircraft and Systems” and ARP 4761 “Guidelines and Methods for conducting the safety assessment process on civil airborne Systems and equipment”:

Abbreviations according to ARP 4761:
FHA – Functional Hazard Assessment
PASA – Preliminary Aircraft Safety Assessment
CCA – Common Case Analysis
PSSA – Preliminary System Safety Assessment
1.3. THE CERTIFICATE IS ISSUED WHEN:
- Compliance with certification requirements has been provided
- Aircraft function or function of its changes and system function meet requirements
- Qualification of parts and systems through inspection and testing is completed
- Flight tests are completed
- Design documents (design data) are available
- Operating instructions (AMM, AFM, etc.) are available
2.) ACC’s SERVICES IN THE AREA OF PRODUCT CERTIFICATIONS OR CHANGES IN PRODUCT CERTIFICATIONS
Development and Certification
- Preperation and evaluation of concept designs
- Product development plan including statement of work (development -> certification -> manufacturing -> after sales) based on ARP 4754A, APQP and other requirements.
- Preperation of certification programs considering certification requirements (certification specification, environmental protection specification, etc.)
- Certification basis
- test planning
- prototyping
- Design Verification
- For aircraft, systems and parts
Safety Analyses and Assessment
- Development and implementation of design safety concepts to identify design weaknesses and single points of failure related to function, systems and parts, as well as means to mitigate design risks according to methodologies as per ARP 4761.
Qualification of parts (incl. ETSO and COTS)
- Planning of test and inspection activities for verification (e.g. development of test plans for parts and components)
Prototyping Activities
- Organization of prototype parts manufacturing
- Establishing of conformity for test articles (e.g. test specimens)
- Preparation for series production
- Re-certification activities (from prototype to new)
- Configuration management in prototyping phase

